In today’s modern world, exposure to toxins is almost unavoidable. From polluted air and contaminated water to processed foods and industrial chemicals, our bodies are constantly fighting against harmful substances. Among the most dangerous of these toxins are heavy metals such as lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium. Over time, these metals can accumulate in the body and disrupt vital biological functions. This growing concern has led many people to explore chelation therapy as a method to cleanse the body and restore balance.
Once used primarily in emergency medical settings, chelation has evolved into a broader therapeutic approach that some practitioners use to support detoxification and overall wellness. Understanding how this therapy works, why it is used, and who it may benefit is essential before considering it as part of a health strategy.
Why Heavy Metal Removal Is Important
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements, but human activity has significantly increased our exposure to them. Unlike essential minerals such as iron or zinc, heavy metals have no beneficial role in the body. Instead, they interfere with enzymes, damage organs, and impair the nervous system.
Long-term accumulation of heavy metals may contribute to:
- Chronic fatigue and brain fog
- Digestive disorders
- Hormonal imbalances
- Weakened immune function
- Cardiovascular problems
- Neurological symptoms such as tremors or memory issues
The body does have natural detoxification systems, primarily the liver and kidneys. However, excessive exposure can overwhelm these systems. This is where heavy metal detox approaches are often considered, especially for individuals with confirmed toxicity or ongoing exposure risks.
Chelation therapy is designed to assist the body by binding to heavy metals and helping eliminate them more efficiently.
What Is Chelation Therapy?
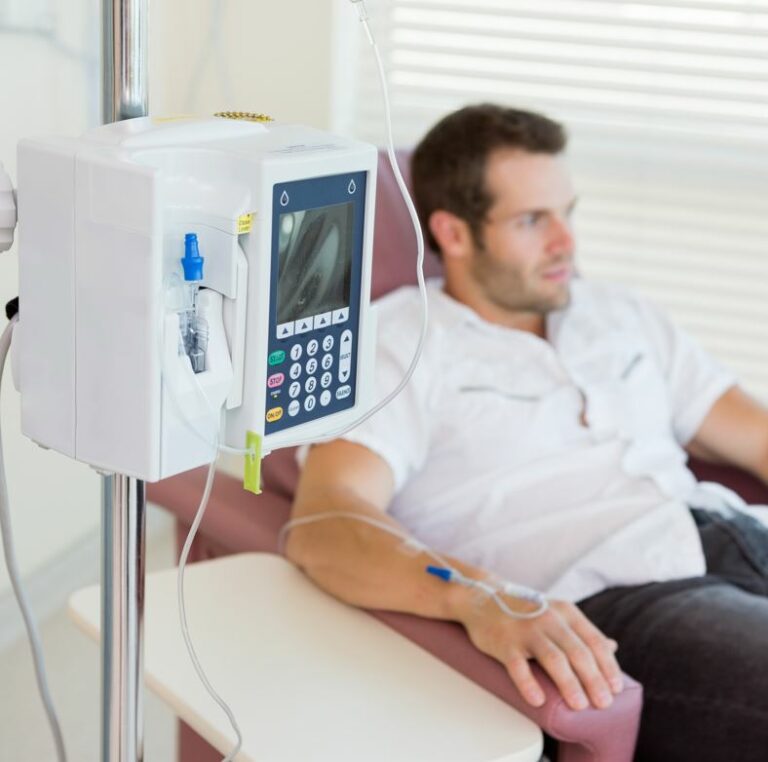
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that uses specific agents, known as chelators, to bind heavy metals in the bloodstream. Once bound, these metals form a stable complex that the body can excrete through urine or, in some cases, bile.
The word “chelation” comes from the Greek word chele, meaning claw, which describes how chelating agents “grab” metal ions. This process prevents metals from interacting with tissues and reduces their toxic effects.
Originally, chelation therapy was developed to treat acute heavy metal poisoning, such as lead exposure in industrial accidents. Today, it is also used in certain integrative and functional medicine practices under careful medical supervision.
How Chelation Therapy Works in the Body
Chelation therapy follows a clear physiological mechanism:
- A chelating agent is introduced into the body, usually intravenously or orally.
- The agent circulates through the bloodstream and seeks out metal ions.
- It binds tightly to heavy metals such as lead, mercury, or cadmium.
- The resulting complex becomes water-soluble.
- The kidneys filter the complex from the blood and excrete it through urine.
This targeted process helps reduce the overall metal burden without directly damaging healthy tissues when properly administered.
Chelation does not “flush everything out” indiscriminately. Instead, it focuses on metals with a strong affinity for the chelating compound being used.
Types of Chelation Therapy
Different types of chelation therapy exist, each suited for specific metals and patient needs. A qualified healthcare provider determines the most appropriate option based on diagnostic testing and medical history.
EDTA Chelation
EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is one of the most commonly used chelating agents. It has a strong affinity for lead, calcium, and certain other metals. EDTA chelation is typically administered intravenously in a clinical setting.
DMSA Chelation
DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid) is often prescribed orally and is commonly used for lead and mercury exposure. It is sometimes preferred for children or individuals who cannot tolerate IV therapy.
DMPS Chelation
DMPS (Dimercaptopropane sulfonate) is used in some countries for mercury and arsenic detoxification. It can be administered orally or intravenously under strict medical supervision.
Natural Chelation Support
While not considered medical chelation, some nutritional approaches support the body’s natural detox pathways. These may include antioxidants, minerals, and dietary changes. However, these methods are not substitutes for medical chelation in cases of confirmed toxicity.
Advantages of Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy offers several potential advantages when used appropriately and under professional guidance.
One of the primary advantages is its targeted action. Unlike generalized detox methods, chelation specifically binds to heavy metals rather than removing beneficial nutrients indiscriminately.
Another advantage is its clinical history. Chelation therapy has been used for decades in conventional medicine for acute poisoning, giving it a well-documented safety profile when protocols are followed correctly.
Additionally, chelation therapy may help reduce the long-term health risks associated with chronic metal exposure, especially in individuals who have occupational or environmental risk factors.
Health Benefits of Chelation Therapy
Many individuals seek chelation therapy for its potential health benefits beyond metal removal. While results vary depending on the individual, some reported benefits include:
- Improved energy levels
- Better mental clarity and focus
- Reduced headaches and muscle pain
- Enhanced immune response
- Improved circulation in some patients
It is important to note that chelation therapy is not a cure-all. The benefits depend on accurate diagnosis, proper dosing, and overall health status. Chelation should always be part of a broader wellness plan that includes nutrition, lifestyle changes, and medical oversight.
Chelation Therapy and Heavy Metal Detox
For people dealing with confirmed toxicity, chelation therapy can be a structured and medically supervised approach to heavy metal detox. Unlike popular detox trends, chelation relies on biochemical principles and laboratory testing.
Before starting therapy, patients typically undergo tests such as blood, urine, or provoked urine testing to identify specific metals and levels. This data-driven approach helps ensure that treatment is necessary and tailored to the individual.
Detoxification through chelation is gradual. Removing metals too quickly can stress the kidneys or cause side effects, which is why protocols emphasize controlled dosing and monitoring.
Step-by-Step Process of Chelation Therapy
Understanding the steps involved can help patients feel more confident and informed.
Step 1: Medical Evaluation
The process begins with a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory testing. This step ensures that chelation therapy is appropriate and safe.
Step 2: Identifying Heavy Metals
Specific tests identify which heavy metals are present and in what quantities. This information determines the type of chelating agent used.
Step 3: Treatment Planning
A customized treatment plan is created, outlining the frequency of sessions, dosage, and duration of therapy.
Step 4: Administration of Chelation Agent
The chelating agent is administered intravenously or orally, depending on the protocol. IV sessions typically last one to three hours.
Step 5: Monitoring and Support
Throughout the therapy, kidney function, mineral levels, and overall health are monitored. Supplements may be recommended to replace essential minerals.
Step 6: Elimination and Recovery
After binding with metals, the body eliminates them naturally through urine. Adequate hydration and rest are essential during this phase.
Safety and Medical Supervision
Chelation therapy should never be self-administered. Improper use can lead to mineral imbalances, kidney stress, or other complications. Working with a licensed medical professional experienced in chelation protocols is critical for safety.
Pregnant women, individuals with kidney disease, or those with certain medical conditions may not be suitable candidates. This reinforces the importance of expert evaluation and ethical medical practice.
Who Should Consider Chelation Therapy?
Chelation therapy may be considered for:
- Individuals with confirmed heavy metal toxicity
- People with occupational exposure (industrial workers, miners, painters)
- Patients with retained metal from medical devices or environmental exposure
- Individuals experiencing unexplained chronic symptoms after thorough evaluation
People often ask, where can i get chelation therapy, and the answer depends on location and regulations. It is typically offered at specialized clinics, integrative medicine centers, or hospitals under qualified physicians. Always verify credentials and treatment standards before proceeding.
Conclusion
Chelation therapy remains a valuable medical tool for removing heavy metals from the body when used responsibly and under expert supervision. By binding toxic metals and supporting their elimination, it can reduce the burden these substances place on vital organs and systems.
While chelation therapy is not suitable for everyone, it plays an important role in modern detoxification strategies for those with documented exposure. When combined with proper nutrition, lifestyle changes, and medical guidance, it can support long-term health and recovery.
Anyone considering chelation should prioritize evidence-based care, transparent communication with healthcare providers, and realistic expectations about outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is chelation therapy scientifically supported?
Yes, chelation therapy is scientifically recognized for treating heavy metal poisoning. Its use beyond acute poisoning should always be guided by evidence, testing, and medical expertise.
How long does chelation therapy take?
Treatment duration varies. Some patients require a few sessions, while others may need several months, depending on metal levels and overall health.
Are there side effects?
Possible side effects include fatigue, headaches, or mild discomfort during treatment. Serious side effects are rare when therapy is properly supervised.
Can chelation therapy remove all toxins?
Chelation therapy specifically targets heavy metals. It is not designed to remove all toxins or replace the body’s natural detox systems.
Is chelation therapy painful?
Most patients experience minimal discomfort. IV insertion may cause slight pain, but the procedure itself is generally well tolerated.